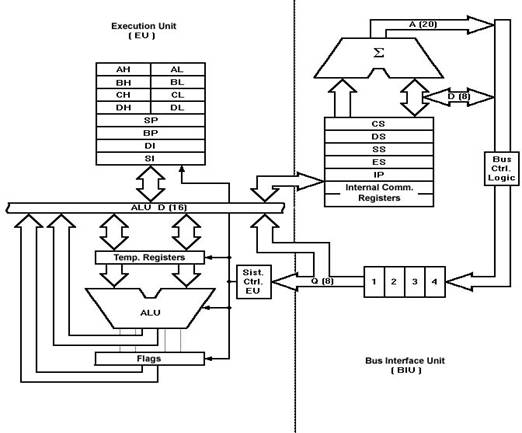
The Execution Unit (EU):
The main components of the EU are General purpose
registers, the ALU, Special purpose registers, Instruction Register and
Instruction Decoder and the Flag/Status Register.
1. Fetches
instructions from the Queue in BIU, decodes and executes arithmetic and logic
operations using the ALU.
2. Sends
control signals for internal data transfer operations within the
microprocessor.
3. Sends
request signals to the BIU to access the external module.
4. It
operates with respect to T-states (clock cycles) and not machine cycles.
8086 has four 16-bit general purpose registers AX,
BX, CX and DX. Store intermediate values during execution. Each of these have
two 8 bit parts (higher and lower).
·
AX register:
It holds operands and results during multiplication and division operations. Also,
an accumulator during String operations.
·
BX register:
It holds the memory address (offset address) in indirect addressing modes.
·
CX register:
It holds count for instructions like loop, rotate, shift and string operations.
·
DX register:
It is used with AX to hold 32-bit values during multiplication and division.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (16 bit):
Performs 8 and 16 bit arithmetic and logic operations.
Special purpose registers (16-bit):
·
Stack Pointer:
Points to Stack top. Stack is in Stack Segment, used during instructions like
PUSH, POP, CALL, RET etc.
·
Base Pointer:
BP can hold offset address of any location in the stack segment. It is used to
access random locations of the stack.
·
Source Index:
It holds offset address in Data Segment during string operations.
·
Destination Index:
It holds offset address in Extra Segment during string operations.
Instruction Register and Instruction Decoder:
The EU fetches an opcode from the queue into the instruction register. The
instruction decoder decodes it and sends the information to the control circuit
for execution.
Flag/Status register (16 bits):
It has 9 flags that help change or recognize the state of the microprocessor.
6 Status flags:
1. carry
flag (CF)
2. parity
flag (PF)
3. auxiliary
carry flag (AF)
4. zero
flag(Z)
5. sign
flag(S)
6. overflow
flag (O)
Status flags are updated after every arithmetic and logic
operation.
3 Control flags:
1. trap
flag (TF)
2. interrupt
flag (IF)
3. direction
flag (DF)
These flags can be set or reset using control instructions
like CLC, STC, CLD, STD, CLI, STI, etc.
Bus Interface Unit:
It provides the interface of 8086 to external memory and
I/O devices via the System Bus. It performs various machine cycles such as
memory read, I/O read etc. to transfer data between memory and I/O devices.
BIU performs the following functions-
·
It generates the 20-bit physical address for memory
access.
·
It fetches instructions from the memory.
·
It transfers data to and from the memory and I/O.
·
Maintains the 6-byte prefetch instruction queue (supports pipelining).
BIU mainly contains the 4 Segment registers,
the Instruction Pointer, a prefetch queue and an Address Generation Circuit.
Instruction Pointer (IP):
·
It is a 16-bit register. It holds offset of the next
instructions in the Code Segment.
·
IP is incremented after every instruction byte is fetched.
·
IP gets a new value whenever a branch instruction occurs.
·
CS is multiplied by 10H to give the 20-bit physical
address of the Code Segment.
·
Address of the next instruction is calculated as CS x 10H
+ IP.
Example:
CS = 4321H IP =
1000H
then CS x 10H =
43210H + offset = 44210H
This is the address of the instruction.
Code Segment register:
CS
holds the base address for the Code Segment. All programs are stored in the
Code Segment and accessed via the IP.
Data Segment register:
DS holds the base
address for the Data Segment.
Stack Segment register:
SS holds the base
address for the Stack Segment.
Extra Segment register:
ES holds the base
address for the Extra Segment.
Address Generation Circuit:
·
The BIU has a Physical Address Generation Circuit.
·
It generates the 20 bit physical address using Segment and
Offset addresses using the formula:
·
Physical Address
= Segment Address x
10H + Offset Address
6 Byte Pre-fetch Queue:
·
It is a 6-byte queue (FIFO).
·
Fetching the next instruction (by BIU from CS) while
executing the current instruction is called pipelining.
·
Gets flushed whenever a branch instruction occurs.



![জাভাস্ক্রিপ্ট-৬ [কমেন্ট, অপারেটর]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhyb8n_zvJUyWrdYaZlstACeLt5P2QU4AFzxuIhSFoEStv2aKMKiPKY3YhV4sbNlINE6CDRduDEOhcz6aIvrSfbIQUJoaYRFlN74DWmJdp8AHGGBrebktvrCLsw1AEExtqjOT7Ef6ayrOPt2Xu0K5pgUr4CqOt04lImf4bl7kvu5e4UE3NVz0hTLzb0tX7i/s72-w370-c-h277/image.png)
![পাইথন প্রোগ্রামিং ল্যাঙ্গুয়েজ দিয়ে দ্বিঘাত সমীকরণ বের করার জন্য প্রজেক্ট [পাইথন-১৫]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi-FUX-7-HvI8Q3HM6OHtkr77HOo4IRopsPklC29WEd67doy1ySl8WwSGH2fn6SKlteo3q9b8ivKD7XdE3ZE-L6v1XfCVxFHHjuSooXeo5ZLsy2dHpbTLUuBRzj35Fvfvb7yJE6j6nToNpoEQHX-qJ1Ydiieix555Gwh9EXnzobiUqcog8mfAbdKgR1-JUz/s72-c/image.png)
![পাইথন প্রোগ্রামিং ল্যাঙ্গুয়েজ দিয়ে কোন সালকে লিপইয়ার বের করার জন্য প্রজেক্ট [পাইথন-১৪]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjyv2pAoSWWw57vyEikxJZq5t-WV3nrwJA2ivPkV39QAqE_YjX3q_wfQNpU1XxSDjoe13_ZzYw5E5fmKkvPV5sorxVCCOCVa_kvFaUT-hlZvMLElIyEtHiPbgl50qddUt7uDb4Tx0o1_jzfKDYqLnr_kr3wU6GpxqaHBExwFv_k9TiN1vbZkzgM9uTk3UY8/s72-c/image.png)